Cavities (also known as caries or tooth decay) are one of the most common chronic diseases of childhood in the United States. Untreated cavities can cause pain and infections that may lead to problems with eating, speaking, playing, and learning. Children who have poor oral health often miss more school and receive lower grades than children who don’t.
- About 1 of 5 (20%) children aged 5 to 11 years have at least one untreated decayed tooth.
- 1 of 7 (13%) adolescents aged 12 to 19 years have at least one untreated decayed tooth.
- Children aged 5 to 19 years from low-income families are twice as likely (25%) to have cavities, compared with children from higher-income households (11%).
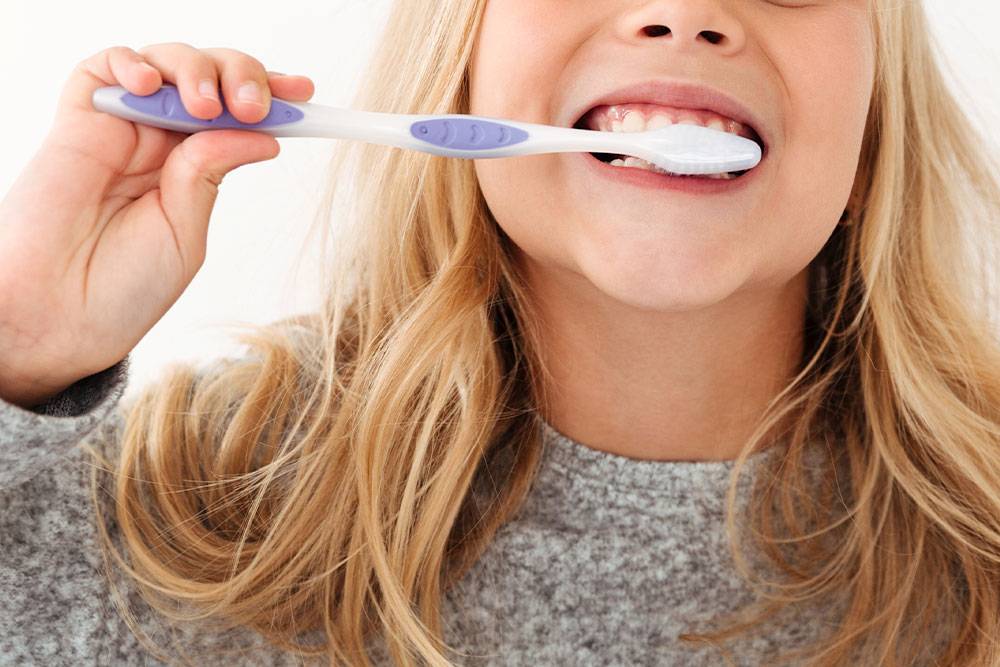
The good news is that cavities are preventable. Fluoride varnish can prevent about one-third (33%) of cavities in the primary (baby) teeth. Children living in communities with fluoridated tap water have fewer cavities than children whose water is not fluoridated. Similarly, children who brush daily with fluoride toothpaste will have fewer cavities.
Dental sealants can also prevent cavities for many years. Applying dental sealants to the chewing surfaces of the back teeth prevent 80% of cavities.
Help develop positive oral health habits with this fun Children’s Oral Healthy Activity Book!
What Parents and Caregivers Can Do
For babies




For children


If your child is younger than 6, watch them brush. Make sure they use a pea-sized amount of toothpaste and always spit it out rather than swallow. Help your child brush until they have good brushing skills.
To see if your community’s water is fluoridated, you can view your water system on CDC’s My Water’s Fluoride website. You can also call your water utility company and request a copy of the utility’s most recent “Consumer Confidence Report.” This report provides information on the level of fluoride in your drinking (tap) water.
If your drinking water does not have enough fluoride to prevent cavities (the optimal amount of 0.7 milligrams per Liter), ask your dentist, pediatrician, family doctor, or nurse if your child needs oral fluoride supplements, such as drops, tablets, or lozenges.
What Are the Risk Factors for Cavities?
Your child’s chance of getting cavities can be higher if:
- Family members (older brothers, sisters, or parents) have cavities.
- They eat and drink a lot of sugary foods and drinks, like soda, especially between meals.
- They have special health care needs.
- They wear braces or orthodontics or oral appliances.
If any of these apply to your child, be sure to talk with your dentist, pediatrician, or family doctor to make sure you are taking extra steps to protect your child’s teeth.